Measurement methods according to DIN ISO 9044
Wire meshes are geometric structures. They can be precisely calculated in advance via the wire diameter and aperture width and matched to the respective application by selecting the appropriate material. DIN/ISO 9044 explains the important terms for testing wire mesh.
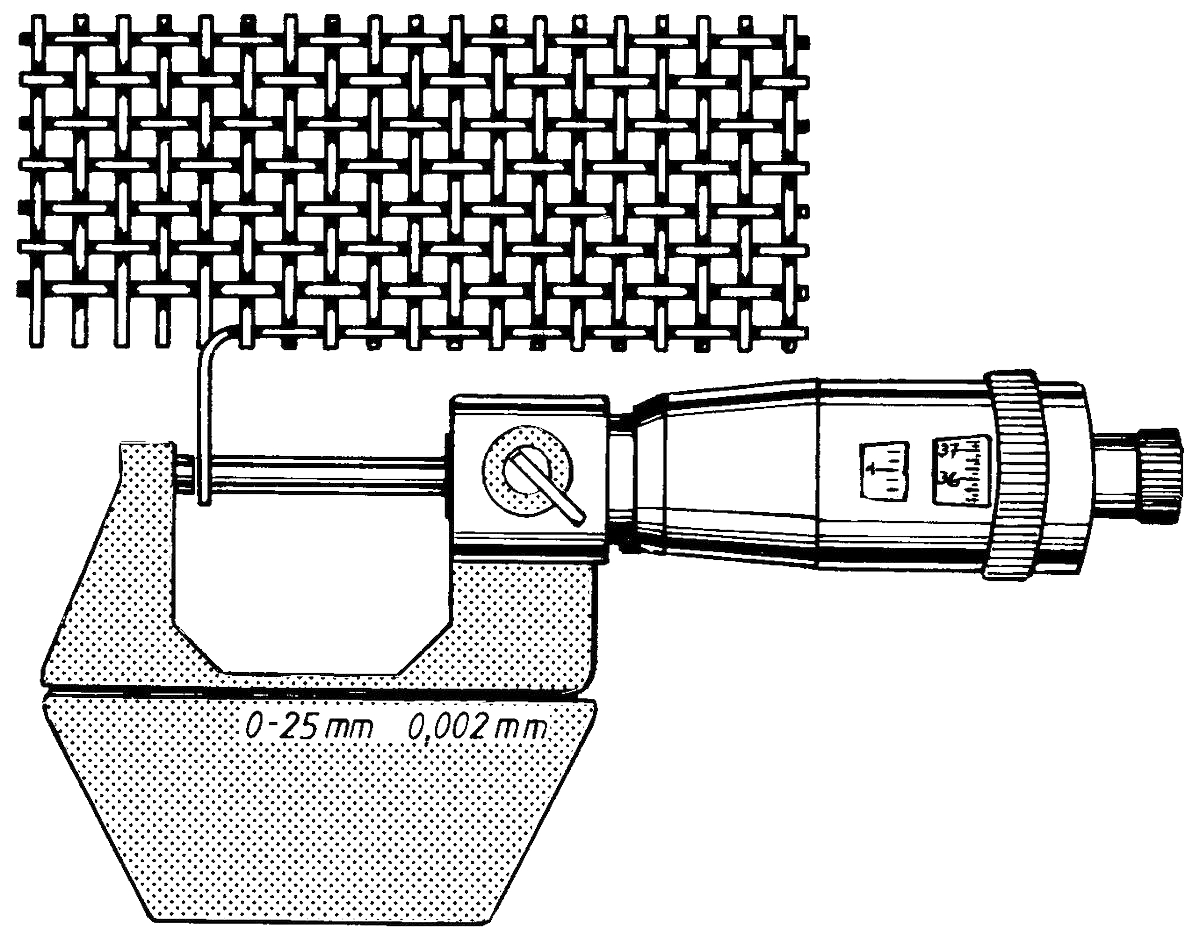
Wire diameter, d
The wire diameter after weaving may be determined by using one of the following methods:
- by measuring wires which have been loosened from the wire cloth (e.g. using a micrometer screw).
- by measuring the wires in the cloth, as far as there is enough space for the measuring instrument.
- by an optical projection method or a scanning method.
The tolerance of the wire before weaving can no longer be determined in the woven wire cloth because of its severe deformation during weaving. However, the nominal wire diameter processed can be calculated using an empirical formula. We are happy to advise you.
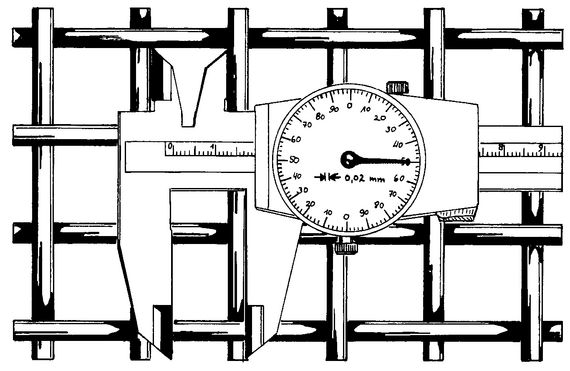
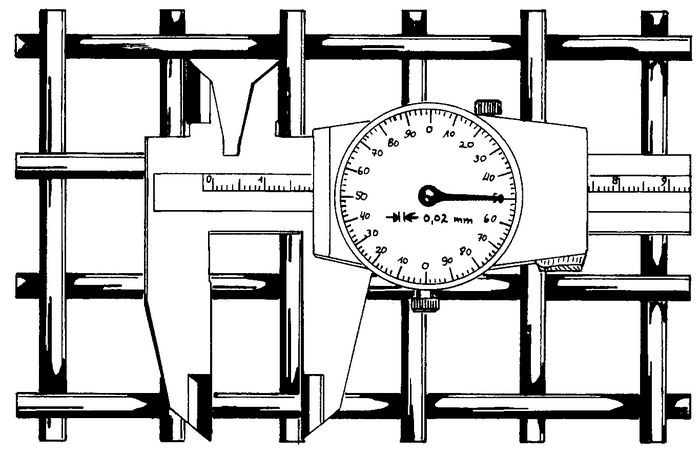
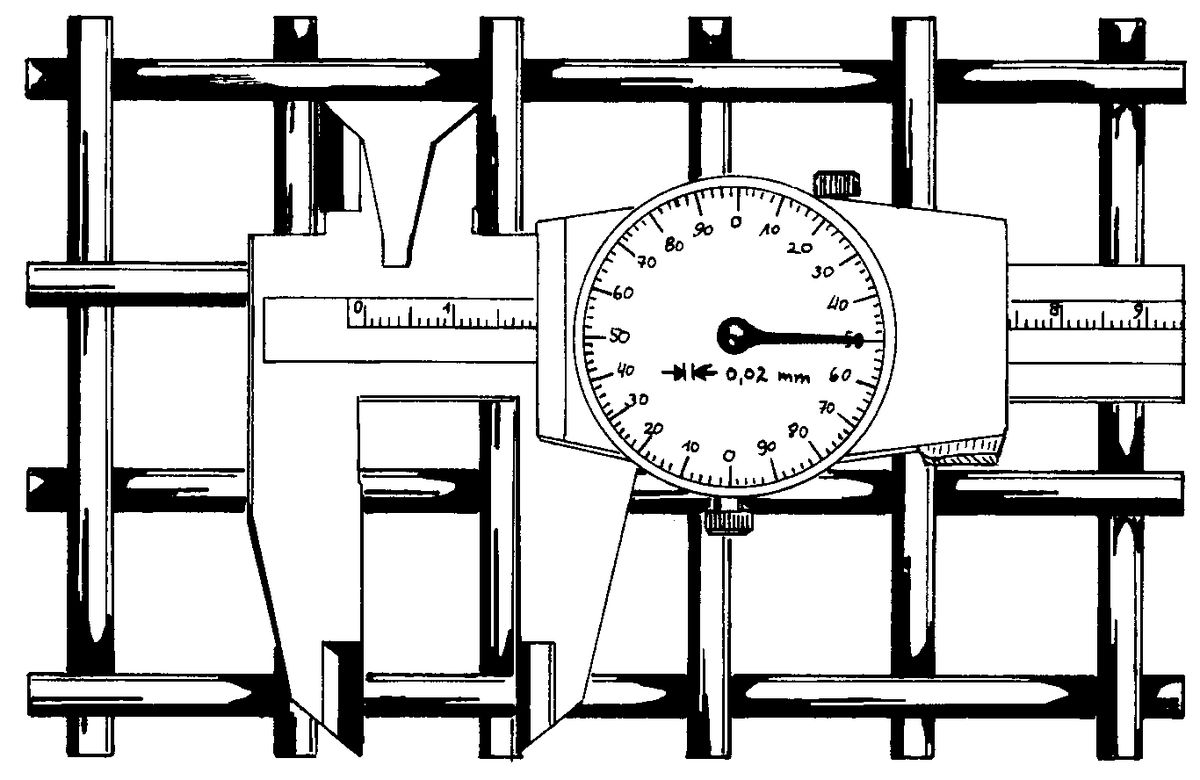
Aperture size: w
The easiest way to determine the aperture size is to use the measuring row method. The number of pitches (p) for a given length (L) is determined. This length is divided by the number of ptiches, which gives the mean value of the divisions. Subtracting the wire diameter (d) from the average pitch gives the aperture size (w).
To obtain the arithmetic mean value of the aperture sizes as many pitches must be measured as are necessary to obtain a reliable statistical value.
For aperture sizes between 16 and 1 mm, 10 pitches should be counted, for smaller aperture sizes up to 0.1 mm, 20 pitches should be counted.